- In other words protons that passes through the channel will not move directly to the matrix. However this channel is not a direct channel.

The Electrochemical Proton Gradient And Atp Synthase Learn Science At Scitable
Proton transfer through ATP-synthase measured by electrochromic carotenoid bandshift and by pH-indicators and ATP release measured by luminescence of luciferin-luciferase were monitored.

. The role of the proton gradient is not to form atp but to release it from the synthase this is a good thing to know. Adenosine triphosphate ATP synthase produces ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate at the expense of proton- or sodium-motive force across the respective coupling membrane in Archaea Bacteria and Eucarya. Proton flow through the ATP synthase enzyme.
These changes are necessary. State whether ATP would end up in the thylakoid or outside of it. Label the areas of high H concentration and low H concentration.
These amazing enzymes thus function as molecular engines that harness the energy derived from proton flow to drive phosphorylation of ADP producing ATP that can be utilized by any number of enzymes to facilitate catalysis of. OSCP and the Proton Channel Rodney J. ATP synthesis by chemiosmosis requires a membrane proton pump a proton gradient and the ATP Synthase.
It creates a hydrophilic channel across the inner mitochondrial membrane that allows a flux of protons that moves down an electrochemical gradient. O provides the energy for adding a phosphate to ADP to make ATP. According to the chemiosmotic theory proton pumps and ATP synthases are coupled by lateral proton flow through aqueous phases.
A provides the energy for adding a phosphate to ADP to make ATP. The subunits of the catalytic portion of the ATP synthase involved in activation as well as the effects of nucleotides are discussed. The ratio between the amount of protons translocated by F0F1 and the ATP yield decreased with the flash number from an apparent value of 13 after the first flash to about 5.
O provides the free energy needed for ADP to bind to the enzyme. Cproduces local pH changes in the active site which alter the equilibrium constant for the reaction. The proton gradient is necessary for ATP synthesis because proton flow through the enzyme causes conformational changes that convert a T subunit into an O subunit with the subsequent release of atp.
Can ATP synthase work without a proton gradient. Biology questions and answers. The relation of activation to proton flux through the ATP synthase and to changes in the structure of enzyme induced by the proton electrochemical gradient are also presented.
1 Nearest neighbor interaction between pumps and ATP synthases. During the process of ____ energy stored in a proton gradient is used to synthesize ATP from ADP and Pi. Devenish1 Mark Prescott1 Glen M.
5 2000 The Oligomycin Axis of Mitochondrial ATP Synthase. These H ions are then used as an energy source during the enzymatic reaction that converts ADP Pi to ATP. The final step of the Krebs cycle is the regeneration of oxaloacetate which is produced when NAD is reduced to _____.
Cation flow through the intrinsic membrane portion of this enzyme Fo subunits ab2c9-12 and substrate turnover in the headpiece F1 subunits alpha3beta3. Journal of Bioenergetics and Biomembranes Vol. This computer model shows the four parts of ATP synthase each part consisting of a number of polypeptide subunits the structure in gray is still an area of active research.
However ATP does not leave the catalytic site unless protons flow through the enzyme. Show the direction protons flow through the enzyme and show the reaction where ATP is synthesized. It is concluded that the gamma and epsilon subunits of CF 1 play.
In case of synthesis the energy input comes from protonic flux through F O downhill the transmembrane electrochemical proton potential difference. The ATP synthase in Figure 914 is using the flow of protons down their concentration gradient no energy is required and this is passive transport. The rate of incorporation of 18O into Pi showed that about equal amounts of bound ATP and ADP are in equilibrium at the catalytic site even in the absence of a proton gradient.
EXplain whythe thylakoids in the experiment were able to make ATP in the dark. Coupling of proton flow and rotation in the F 0 motor of ATP synthase was investigated using the thermophilic Bacillus PS3 enzyme expressed functionally in Escherichia coli cells. Provides the energy for adding a phosphate to ADP to make ATP.
The protons flow through the ATP synthase enzyme complex which crosses the lipid matrix of membranes. ATP synthase uses the protons flowing into the matrix to bind ADP and P i and release ATP. The ATP synthase F 1-ATPase is attached to the F o protein on the inside of the matrix.
The respiratory chain and atp synthase are separate. F0F1 ATP synthases synthesize ATP in their F1 portion at the expense of free energy supplied by proton flow which enters the enzyme through their channel portion F0. Three long-standing challenges to this concept were examined in the light of experiments carried out with thylakoids.
In case of hydrolysis the enzyme functions as an ATP-driven proton pump and generates. Considerable effort has been devoted in recent years to determining the structure and molecular mechanism of the ATP synthase. The flow of H through the ATP synthase complex in favor of the H gradient is responsible for changes in the configuration of the CF 1 subunit.
The F 1-ATPase is named by the reverse reaction it catalyzes when it is isolated from mitochondria and thus uncoupled from the proton gradient. It is driven by the proton motive force generated during the flow of electrons from the light stage. Proton flow through the ATP synthase enzyme provides the free energy needed for ADP to bind to the enzyme.
Produces local pH changes in the active site which alter the equilibrium constant for the reaction. ATP is synthesized as _____ flow down their concentration gradient through ATP synthase. The energy released in the process activates ATP synthase and it catalyses ATP synthesis.
The ATP synthase is an enzyme located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. - The only way for protons to enter is the ATP synthase specially the a subunit which contains a proton channel. ATP synthase catalyzes ATP synthesishydrolysis coupled to transmembrane proton transfer.
Like hydroelectric turbines ATP synthase components rotate in response to the proton flow and this rotational energy is then coupled to ATP synthesis. The smaller subunits of F1 especially subunit delta may act as energy transducers between these rather distant functional units. The transmembrane channel of ATP synthase facilitates the diffusion of protons back to the mitochondrial matrix.
Bresults in the release of ATP from its tightly bound state in the active site. Two protons pass through the F 0 channel from intermembrane. Click to see full answer.
Cysteine residues introduced into the N-terminal regions of subunits b and c of ATP synthase bL2CcS2C were readily oxidized by treating the expressing cells with CuCl 2 to. Alternatively since the ATP synthase is a reversible proton pump during hydrolysis of ATP protons will flow through Fo in the opposite direction and thus generate a OAH. Proton flow through the ATP synthase enzyme results in the release of ATP from its tightly bound state in the active site.
Boyle2 and Phillip Nagley13 Oligomycin has long been known as an inhibitor of mitochondrial ATP synthase putatively binding the Fo subunits 9 and 6 that contribute to. What happens actually is that protons will face a C subunit.

Structure Of The Proton Channel Subunits Of E Coli Atp Synthase A Download Scientific Diagram
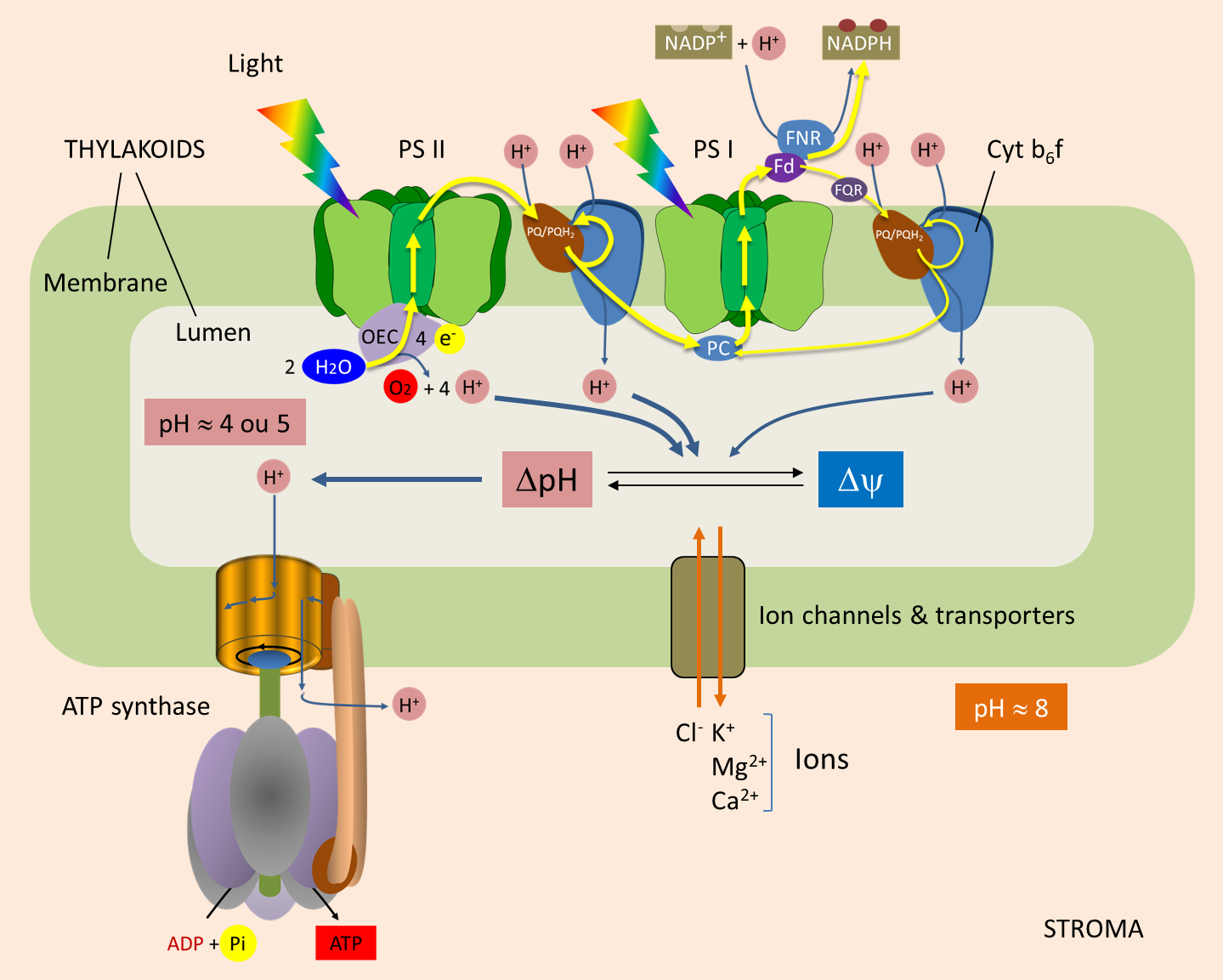
Atp Synthesis Encyclopedia Of The Environment

What Is The Relation Between Chemiosmosis And Atp Synthase Quora
0 Comments